Refer to
Heated Oxygen Sensors
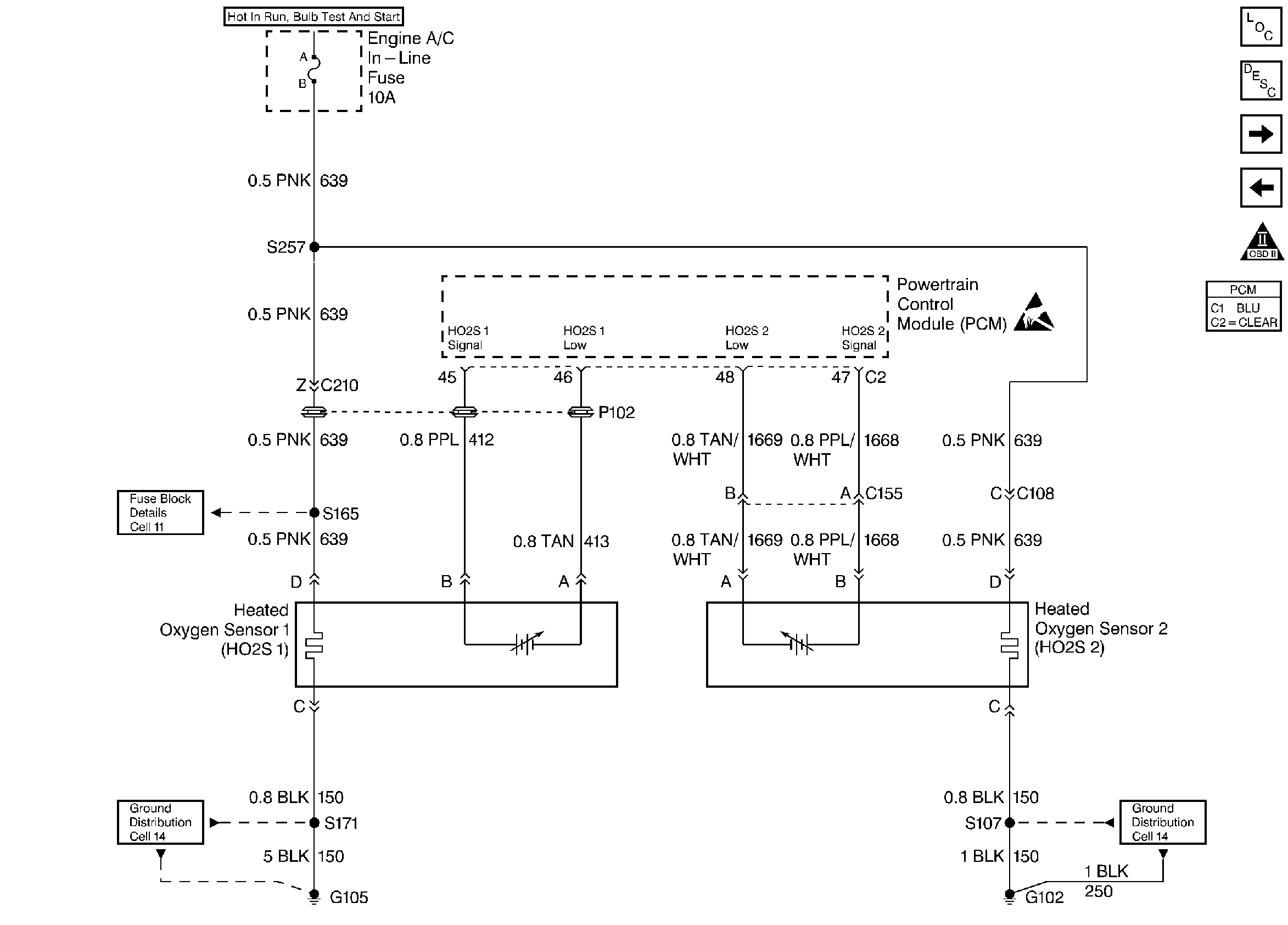
Circuit Description
Heated oxygen sensors are used to minimize the amount of time required for closed loop fuel control operation and to allow accurate catalyst monitoring. The oxygen sensor heater greatly decreases the amount of time required for fuel control sensor HO2S 1 to become active. The oxygen sensor heater is required by catalyst monitor sensor HO2S 2 to maintain a sufficiently high temperature. This allows accurate exhaust oxygen content readings further from the engine.
The PCM will run the heater test only after a cold start (determined by engine coolant and intake air temperature at the time of startup) and only once during an ignition cycle. When the engine is started the PCM will monitor the HO2S voltage. When the HO2S voltage indicates a sufficiently active sensor, the PCM looks at how much time has elapsed since startup. If the PCM determines that too much time was required for the HO2S 1 to become active, a DTC P0135 will set. The time it should take the HO2S to reach operating temperature is based on the engine coolant temperature at start-up and the average Mass Air Flow since startup (higher average airflow or higher startup engine coolant temperature = shorter time to HO2S activity).
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | No active misfire, fuel injector circuit, TP sensor, EVAP, IAT sensor, MAP sensor, Fuel trim, EGR, ECT sensor, MAF sensor or CKP sensor DTC(s) present. |
| • | Intake Air Temperature (IAT) is less than 100°C (212°F) at startup. |
| • | Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is less than 100°C (212°F) at startup. |
| • | IAT and ECT are within 5°C (18°F) of each other at start-up. |
| • | Average mass airflow for the sample period is less than 28 gm/s. |
| • | HO2S 1 voltage remains within 150 mV of the bias voltage (about 450 mV) for a longer amount of time than it should. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) during the second consecutive trip in which the diagnostic test has been run and failed. |
| • | The PCM will store conditions which were present when the DTC set as Freeze Frame and Failure Records data. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn OFF the MIL during the third consecutive trip in which the diagnostic has been run and passed. |
| • | The History DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles have occurred without a malfunction. |
| • | The DTC can be cleared by using the scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
| • | Poor connection at PCM. Inspect harness connectors for backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal to wire connection. |
| • | Damaged harness. Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the display on the scan tool while moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change in the display will indicate the location of the fault. |
Reviewing the Fail Records vehicle mileage since the diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the condition.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table.
-
The HO2S should be allowed to cool before performing this test. If the HO2S heater is functioning, the signal voltage will gradually increase or decrease as the sensor element warms. If the heater is not functioning, the HO2S signal will remain near the 450 mV bias voltage.
-
Checks that the ignition feed circuit to the HO2S is not open or shorted. The test light should be connected to a good chassis ground, in case the HO2S low or HO2S heater ground circuit is faulty.
-
Checks the HO2S heater ground circuit.
-
Checks for an open or shorted HO2S heater element. The heater element resistance will vary according to HO2S temperature (a hot HO2S heater element will measure a much higher resistance than a HO2S heater element at room temperature). It is important to allow the HO2S to cool before measuring HO2S heater element resistance.
-
An open HO2S signal or low circuit can cause the HO2S heater to appear faulty. Check these circuits before replacing the sensor.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic system check performed? | -- | Go to Powertrain OBD System Check | |
|
Important: If engine has just been operating, allow engine to cool for about one half hour before proceeding. Ignition ON, engine OFF, monitor HO2S 1 voltage on the scan tool HO2S data list. Does HO2S voltage go from bias voltage to greater than the first specified value or less than the second specified value? | 600 mV 300 mV | Refer to Diagnostic Aids | ||
3 | Inspect fuse for HO2S 1 ignition feed. Is the fuse open? | -- | ||
Does test light illuminate? | -- | |||
Connect test light between HO2S 1 ignition feed and HO2S 1 heater ground. Does test light illuminate? | -- | |||
Is HO2S heater resistance within the specified values? | 3 - 10 ohms | |||
7 | Repair open HO2S 1 ignition feed circuit to HO2S 1 (refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) Repair -5). Is action complete? | -- | -- | |
8 | Repair open HO2S 1 heater ground circuit (refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) Repair-5). Is action complete? | -- | -- | |
9 |
Was a poor connection found? | -- | ||
10 |
Was a problem found? | -- | ||
Check for a poor HO2S 1 signal or low circuit terminal connection at the HO2S 1 harness connector and replace terminal(s) if necessary (refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) Repair section 8A-5). Did any terminals require replacement? | -- | |||
12 | Check for poor HO2S 1 low circuit terminal connection at the PCM and replace terminal if necessary (refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) Repair-5). Did the terminal require replacement? | -- | ||
13 | Check for poor HO2S 1 signal circuit terminal connection at the PCM and replace terminal if necessary (refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) Repair-5). Did the terminal require replacement? | -- | ||
14 | Replace HO2S 1. Is action complete? | -- | -- | |
15 | Locate and repair short to ground in HO2S 1 ignition feed circuit and replace faulty fuse (refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) Repair-5). Is action complete? | -- | -- | |
16 | Important: If engine has just been operating, allow engine to cool for about one half hour before proceeding.
Does HO2S voltage go from bias voltage to greater than the first specified value or less than the second specified value? | 600 mV 300 mV | Repair complete |
